How OpenAI and Anthropic Are Cashing In on AI: A Look at Their Revenue Models
October 31, 2024 | by Furqan
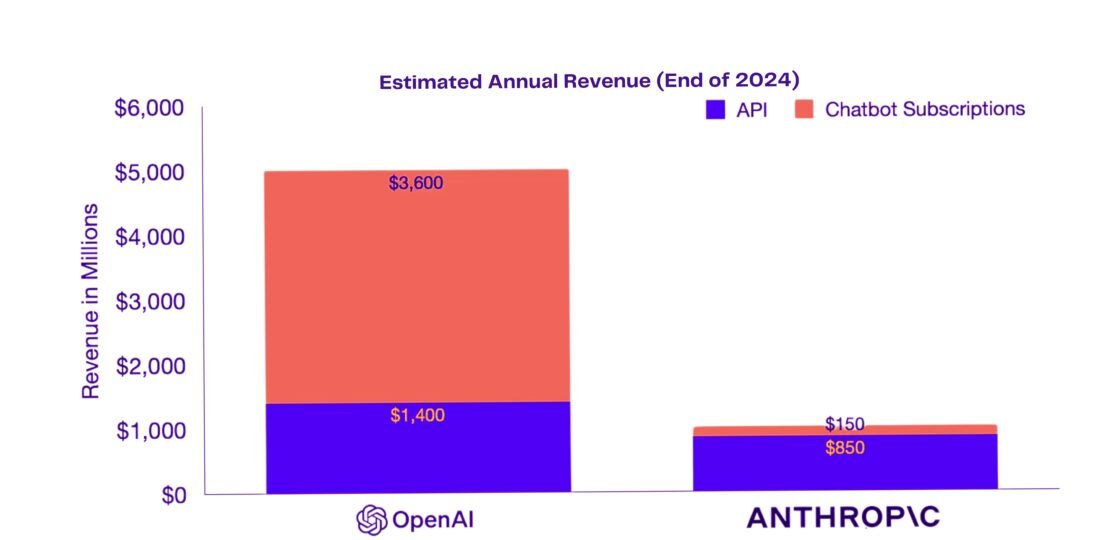
As artificial intelligence technologies expand in both functionality and market reach, companies like OpenAI and Anthropic lead the charge, developing models that serve diverse applications. Two recently shared visuals provide insights into their estimated revenue streams by the end of 2024, illustrating the impact of APIs and chatbot subscriptions on their annual revenue. Here’s an in-depth analysis of how each company generates revenue and what these numbers reveal about their business models and strategic focuses.
Revenue Projections for OpenAI and Anthropic (End of 2024)
The above chart details the Estimated Annual Revenue for both OpenAI and Anthropic by the end of 2024. OpenAI stands out with an impressive projected revenue of $5 billion, derived from two primary sources: API usage and chatbot subscriptions. The breakdown reveals that API-related revenue contributes $1.4 billion, while chatbot subscriptions dominate with $3.6 billion. This significant share from chatbot subscriptions suggests that OpenAI’s consumer-focused offerings, likely including the popular ChatGPT subscription plans, are highly successful in monetizing individual users and enterprises who leverage OpenAI’s chatbot technology.
In contrast, Anthropic’s projected revenue is much smaller in scale, estimated at $1 billion. However, Anthropic’s revenue is heavily weighted towards API-related services, generating $850 million from API usage and a mere $150 million from chatbot subscriptions. This division indicates Anthropic’s primary focus on embedding its AI technologies within other systems and applications rather than focusing on consumer-oriented chatbot subscriptions.

Revenue Breakdown by Percentage
The above chart, OpenAI vs Anthropic Projected Revenue Analysis, provides a percentage-based comparison of the revenue sources for each company. OpenAI’s revenue composition shows that 73% stems from chatbot subscriptions, while 27% comes from API services. This breakdown underscores OpenAI’s success in building a strong subscriber base around its chatbot, with a comparatively smaller but still substantial revenue from API integrations.
Anthropic, however, shows an almost opposite split. A striking 85% of its revenue comes from API usage, while only 15% derives from chatbot subscriptions. This revenue model aligns with a strategy focused on API partnerships, emphasizing Anthropic’s commitment to supporting businesses and developers rather than direct-to-consumer chatbot solutions.
Key Takeaways
- Consumer vs. Developer Focus:
- OpenAI’s revenue heavily relies on chatbot subscriptions, suggesting a successful consumer-oriented approach. The high percentage from chatbot subscriptions indicates that OpenAI has effectively monetized its AI-powered chat services, appealing to individual users and possibly business teams who use these tools for various tasks, from customer service to personal productivity.
- Anthropic, by contrast, is predominantly API-driven, indicating a focus on enabling other businesses and platforms to leverage its technology. This developer-centric approach may make Anthropic appealing for companies that wish to integrate sophisticated AI capabilities into their existing systems without building proprietary solutions.
- Revenue Potential of Chatbot Subscriptions:
- The data reveals a strong market appetite for chatbot subscriptions, as evidenced by OpenAI’s dominance in this space. This consumer engagement could be a sign of increasing comfort and reliance on conversational AI for personal and professional purposes.
- Anthropic’s lower revenue from chatbot subscriptions may reflect a strategic choice or a less aggressive marketing approach for consumer chatbot products.
- API Revenue as a Stable Foundation:
- Both companies recognize the value of API services, which create recurring revenue streams through partnerships and B2B applications. Anthropic’s emphasis on API revenue may be strategic, aiming to provide flexible AI solutions that businesses can seamlessly embed in their operations, potentially fostering long-term partnerships and integrations.
What This Means for the AI Industry
These revenue models highlight two distinct paths in the AI industry. For companies like OpenAI, a consumer-first model can yield high returns through subscription services. This approach relies on building and maintaining a strong, loyal user base that sees clear value in regular, ongoing AI access.
On the other hand, the success of Anthropic’s API-driven revenue suggests that a B2B approach is equally valid, if not more stable in some ways. By partnering with companies and developers, Anthropic is betting on long-term, scalable relationships that provide reliable income without the unpredictability of consumer behavior.
Final Thoughts
As the year unfolds, OpenAI’s consumer-driven revenue model and Anthropic’s developer-oriented approach will serve as case studies for other AI firms considering their go-to-market strategies. While OpenAI capitalizes on widespread consumer adoption through chatbot subscriptions, Anthropic’s substantial API revenue highlights the resilience and appeal of a business model focused on technology integration. Together, these companies exemplify the diverse pathways to financial success within the rapidly evolving AI industry.
RELATED POSTS
View all


